The construction industry is inherently high-risk due to the nature of its activities, including working at heights, using heavy machinery, and dealing with hazardous materials. Our client, a leading construction company, recognized the need to adopt a more robust safety framework to protect its workforce and achieve the ambitious goal of zero accidents on all project sites. The Clide Zero Accident Process (C-ZAP) was identified as the ideal solution to transform their safety culture and eliminate accidents across multiple large-scale projects.
This case study outlines the systematic, phase-wise implementation of C-ZAP over four years, highlighting the role of data analytics, training, and behavioral safety interventions. This case study outlines the structured approach taken to implement C-ZAP over 4 years. It provides a detailed account of each phase, highlights the data-driven decisions made, and showcases the impact of the project using statistical insights.
Client Industry
Construction
Project Duration
4 Years
Consultant Involved
6 (Total Consultant)
C-ZAP Consulting Project Phases & Approach
Phase 1 - Gap Assessment (First 6 months)
The project began with a comprehensive gap analysis to understand the current safety landscape and challenges:
- Site Safety Audits: Conducted across all active construction sites to assess the effectiveness of existing safety protocols.
- Incident Review: Analyzed accident and near-miss data from the past three years to identify patterns and common causes.
- Safety Culture Assessment: Interviewed workers, supervisors, and project managers to evaluate safety awareness and the existing reporting culture.
- Risk Profiling: Identified high-risk tasks such as crane operations, scaffolding work, and trench excavation.
Phase 1 - Key Findings
Safety Practices
Inconsistent safety practices across different sites.
Hazard Management
Limited proactive hazard identification processes.
Safety Reporting
Low reporting rates of near misses, with workers hesitant to report minor incidents.
Statistical Highlight: Phase 1
65% of recorded incidents were linked to unsafe behaviors rather than equipment failure or technical issues.
Phase 2 - Framing the Strategy (Months 7-12)
With the gap assessment complete, we worked closely with the client’s leadership team to develop a customized C-ZAP strategy . Key elements of the strategy included:
- Leadership Commitment: Secured buy-in from top management to create a safety-first mindset.
- Behavioral Safety Focus: Prioritized behavioral interventions, targeting high-risk activities.
- Zero Tolerance Policy: Implemented a zero-tolerance policy for unsafe practices, setting clear guidelines for compliance.
- Zero Accident Roadmap: Developed a step-by-step roadmap to achieve zero accidents by integrating C-ZAP principles across all projects.
Data Driven Decision : Phase 2
The decision to prioritize crane operations and scaffolding was based on a detailed analysis that revealed these activities contributed to 40% of all serious accidents on site.
Phase 3 - Training & Skill Development (Months 13-24)
Effective implementation of the Clide Zero Accident Process relied heavily on training and capacity building at all levels of the organization:
- Workforce Training Programs: Tailored safety training was provided to over 2,500 employees, focusing on hazard identification, safe equipment usage, and behavioral safety.
- Leadership Safety Training: Senior management and project supervisors underwent specialized training on leading safety initiatives and enforcing the zero-tolerance policy.
- On-the-Job Training: Safety simulations and drills were conducted at various project sites to improve workers’ preparedness for emergency situations.
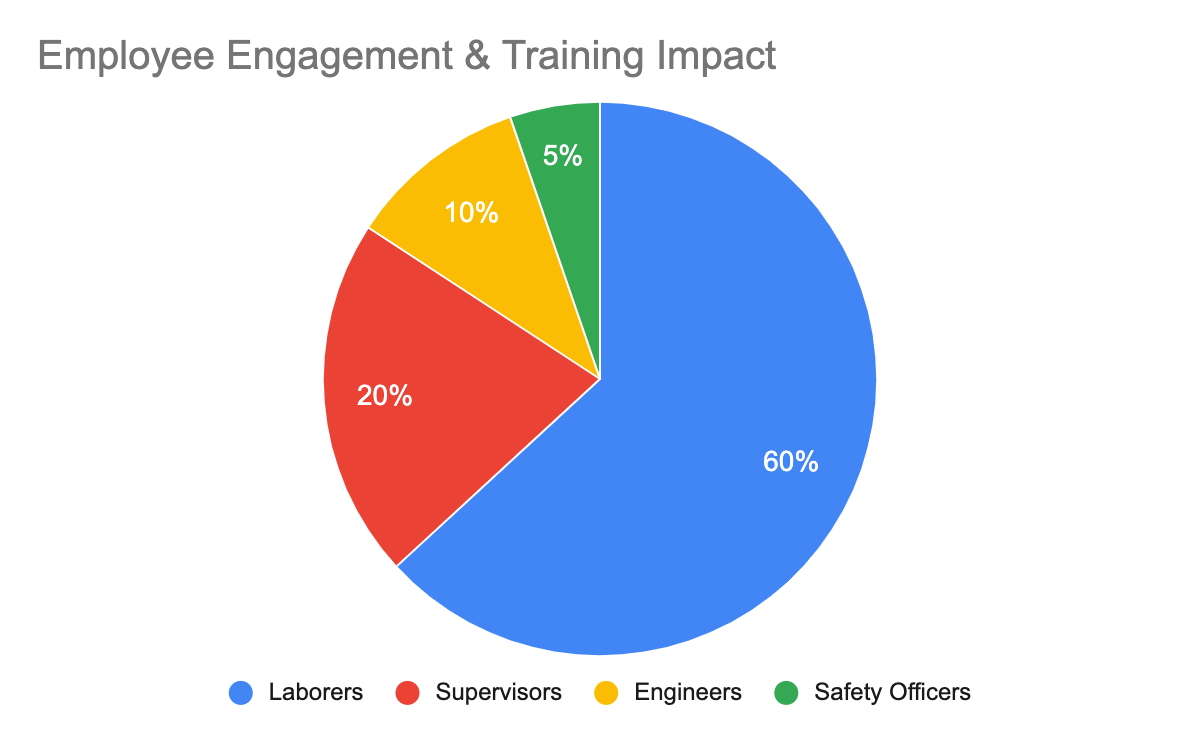
Phase 3 - Key Results
Training
90% of workers demonstrated improved knowledge of safety protocols after training.
Reporting
35% increase in the reporting of near misses following the introduction of safety awareness programs.
Employee Engagement
63% participation increase in safety activities by frontline workers related hazard management.
Statistical Highlight: Phase 3
80% of employees surveyed reported feeling more confident in addressing and reporting unsafe behaviors after completing C-ZAP training.
Phase 4 - Handholding & Implementation Support (Months 25-36)
During this phase, the focus was on handholding and providing on-site support to ensure the effective implementation of C-ZAP principles:
- On-site Safety Consultants: Six consultants were deployed across major construction sites to guide the integration of C-ZAP, offering real-time advice and monitoring.
- Safety Observations: Conducted over 60,000 safety observations, with immediate corrective actions taken on identified unsafe behaviors.
- Behavioral Safety Interventions: Specific interventions were targeted toward high-risk activities like lifting operations and fall prevention.
Data Driven Decision : Phase 4
Based on real-time safety data, shifts with higher fatigue levels showed more safety violations. Adjusting work schedules reduced violations by 25%.
Phase 5 - Review Meetings & Continuous Improvement (Months 37-48)
To ensure the program’s success, regular review meetings were essential for evaluating progress and implementing continuous improvement measures:
- Monthly Safety Review Meetings: All project managers and safety officers met monthly to review safety metrics and discuss areas for improvement.
- Incident Root Cause Analysis: Conducted for all accidents and near misses, with lessons learned shared across teams.
- Continuous Feedback Loop: Collected feedback from workers and supervisors to refine safety interventions and address concerns proactively.
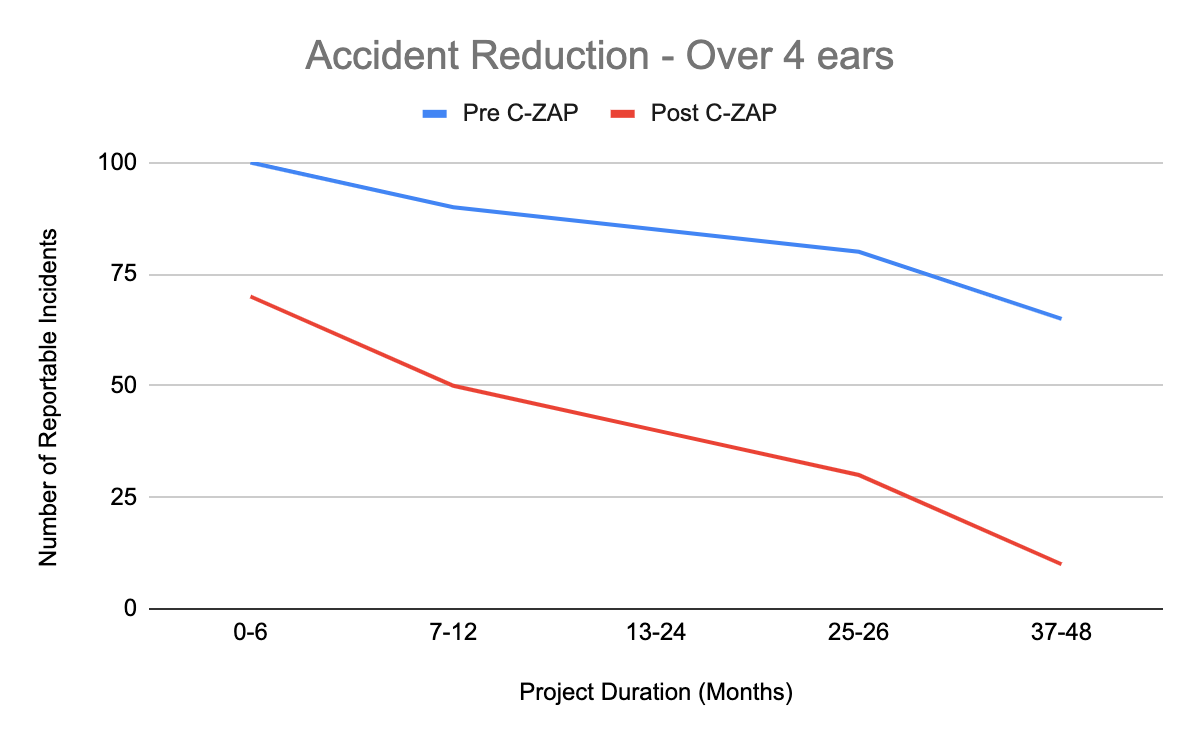
Phase 5 - Key Impact
Zero Incident
Zero fatalities recorded during the last two years of implementation.
Incident Rate
60% reduction in reportable incidents by the end of the fourth year.
Near Miss Reporting
50% increase, signifying a shift toward a more proactive safety culture.
Statistical Highlight: Phase 5
Over the final year of the project, 95% compliance with safety protocols was achieved across all construction sites.
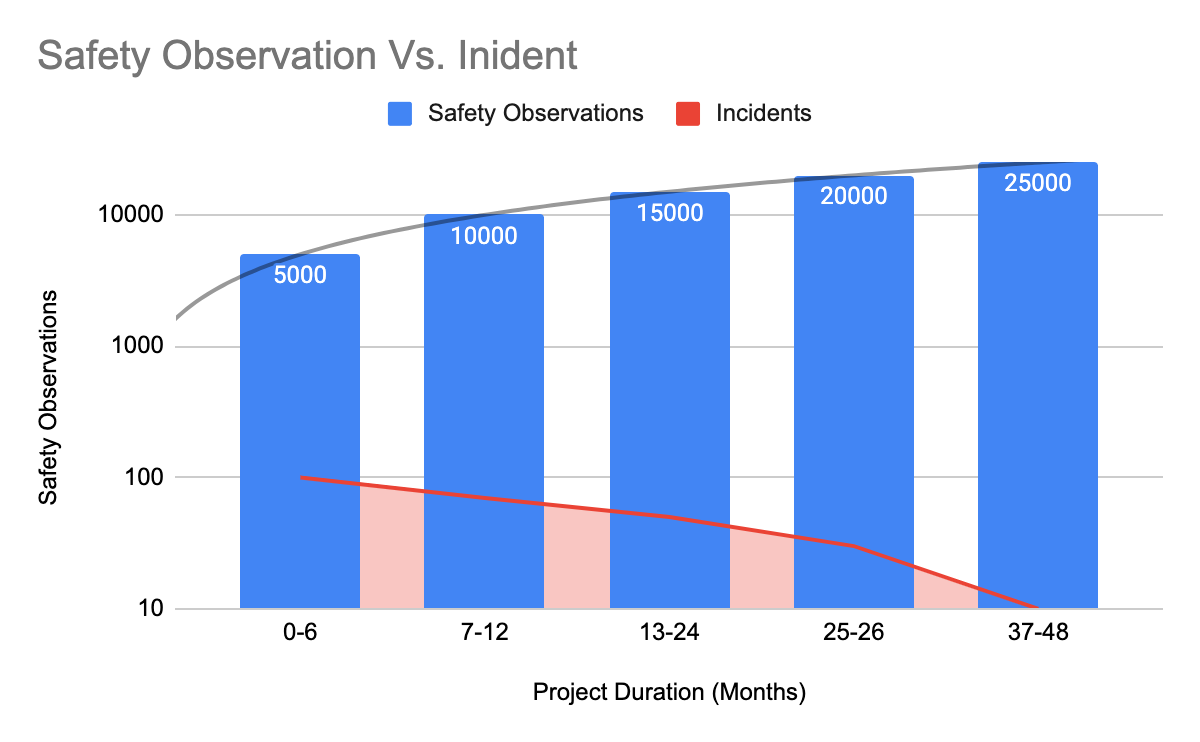
Phase 6 - Data Analytics & Tools (Ongoing)
A critical component of C-ZAP’s success was the integration of data analytics tools to monitor and manage safety performance:
- Real-Time Safety Dashboards: Installed across all sites to track real-time safety data, including incidents, observations, and compliance rates.
- Predictive Analytics: Utilized historical and current data to predict high-risk periods and activities, allowing management to take preemptive safety measures.
- Performance Metrics: Monitored KPIs such as incident rates, near misses, safety observation numbers, and compliance scores.
Data Driven Decision : Phase 6
Predictive analytics highlighted that working at heights during windy conditions posed a higher risk. This led to the implementation of wind monitoring systems on all sites, reducing fall incidents by 30%.
C-ZAP Consulting Project Outcome & Results
The CLIDE Zero Accident Process (C-ZAP) implementation successfully transformed the client’s safety practices, leading to a significant reduction in accidents and fostering a safety-driven culture. Below are the key metrics illustrating the impact of the project.
Accident Reduction
60% reduction in total reportable incidents across all sites.
Compliance Rates
95% adherence to safety protocols by the end of the project.
Near Miss Reporting
50% increase in near-miss reporting, enabling proactive risk management..
Real Time Safety
60,000 safety observations logged, with corrective actions taken in real-time.
The implementation of the Clide Zero Accident Process (C-ZAP) in the construction industry resulted in a substantial improvement in workplace safety, with zero fatalities recorded and a significant reduction in reportable incidents. The integration of data-driven decision-making, robust safety training, and real-time safety monitoring tools were crucial in achieving these results and establishing a sustainable zero-accident culture.